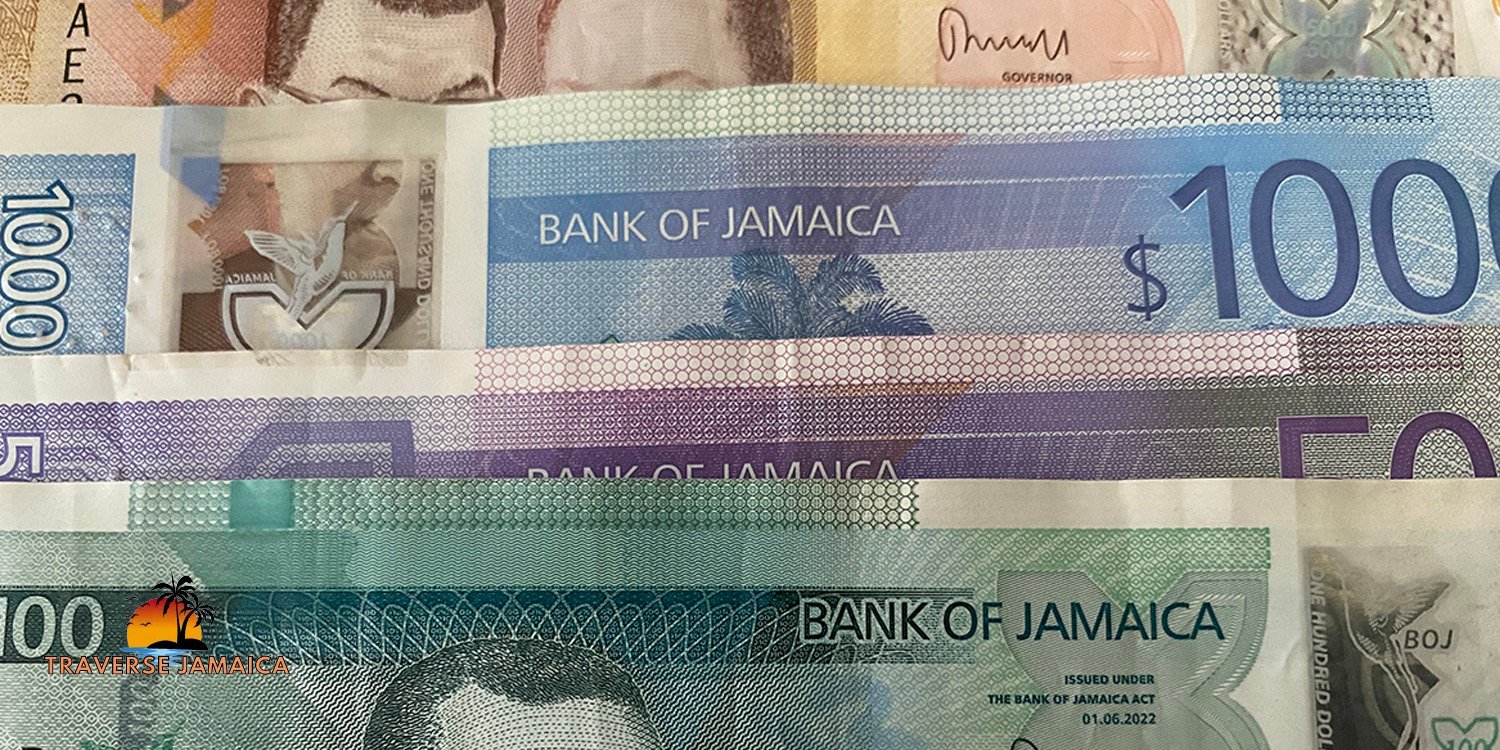Jamaica, an island known for its vibrant culture, stunning beaches, and reggae music, also boasts a fascinating monetary system with a rich historical background. The Jamaican dollar (JMD), introduced after the island gained independence, holds a pivotal role in the country’s economy. Understanding the Jamaican currency offers valuable insight into the country’s economic development, global relations, and cultural symbolism.
1. The Birth of Jamaica’s Currency: A Brief History
Jamaica’s journey towards a national currency began after gaining independence from Britain in 1962. Before this, the island used the British pound, which had been in circulation since the colonial era. The need for a distinct national identity, both culturally and economically, led to the creation of the Jamaican dollar.
- Transition from British Pound to Jamaican Dollar: The official switch from the British currency system occurred on September 8, 1969. The exchange rate was simple: 1 Jamaican dollar (JMD) was equivalent to 10 shillings in the old system.
- Decimalization: This was a part of the move towards decimalization, aligning Jamaica with modern global monetary systems that use units of 10. It allowed for easier transactions and a clearer understanding of value.
2. Denominations and Features of Jamaican Currency
The Jamaican dollar consists of both paper notes and coins. Each is rich in design, featuring iconic Jamaican leaders, national symbols, and landmarks.
Paper Notes
- $50 Bill: Featuring the image of Samuel Sharpe, a national hero who led the Christmas Rebellion, an important moment in the abolition of slavery in Jamaica.
- $100 Bill: Bearing the portrait of Donald Sangster, a former Jamaican prime minister, this is one of the most commonly used notes in circulation.
- $500 Bill: Known as the “Nanny,” this note honors Nanny of the Maroons, a national heroine and leader of the Maroon resistance against the British.
- $1000 Bill: Featuring Michael Manley, a former prime minister known for his progressive policies, this note plays a significant role in the economy.
- $2000 Bill: The newest addition to Jamaica’s currency, the $2000 note features the images of former Prime Ministers Michael Manley and Edward Seaga. This bill commemorates the contributions of these two influential leaders in shaping Jamaica’s political and economic landscape.
- $5000 Bill: Representing Hugh Lawson Shearer, this note is the highest denomination in circulation, used primarily for larger transactions.
Coins
As of now, Jamaican coins come in denominations like $1, $5, $10, and $20, but the $20 coin is not widely used. Higher denominations, like $50, $100, $500, $1,000, and up, are issued as banknotes. Unlike some countries that issue larger value coins for commemorative or collector’s purposes, Jamaica primarily sticks to practical, lower-value coins for everyday transactions.
3. The Role of the Jamaican Central Bank
The Bank of Jamaica (BOJ) is responsible for managing the island’s currency, ensuring monetary stability, and regulating financial institutions. Founded in 1960, the BOJ plays a critical role in monitoring inflation, maintaining reserves, and protecting the value of the Jamaican dollar against foreign currencies.
- Foreign Exchange: The BOJ manages the exchange rate between the Jamaican dollar and major world currencies like the US dollar, British pound, and Euro. The exchange rate fluctuates due to several factors, including economic performance, inflation, and global market conditions.
4. Exchange Rates and the Global Position of the Jamaican Dollar
The Jamaican dollar is considered a soft currency, meaning its value is not as stable or strong compared to the US dollar or Euro. This fluctuation is largely influenced by the country’s economic challenges, such as debt, inflation, and reliance on tourism.
- Depreciation Over Time: Since its introduction in 1969, the Jamaican dollar has depreciated significantly. In the 1970s, 1 JMD was approximately equivalent to 1 USD. Today, 1 USD equals roughly 150 JMD.
- Tourism and Remittances: Jamaica’s economy heavily relies on tourism and remittances, which significantly impact the demand and value of its currency. Tourists exchange foreign currency for Jamaican dollars, fueling a vital part of the economy.
5. Inflation and the Challenges Facing the Jamaican Dollar
Jamaica has faced recurring bouts of inflation over the years, a common challenge for developing economies. Inflation weakens the purchasing power of the Jamaican dollar, leading to higher costs of living and increasing the cost of imports.
- Economic Policies: The Jamaican government and the Bank of Jamaica have implemented measures to stabilize the currency, including fiscal reforms, monetary policies, and seeking assistance from international financial institutions like the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- Currency Devaluation: Despite these efforts, the Jamaican dollar has continued to devalue, creating challenges for trade and increasing the cost of imported goods, which form a large part of Jamaica’s economy.
6. Cultural Significance of the Jamaican Dollar
Beyond its economic role, the Jamaican dollar serves as a symbol of national pride and identity. The figures depicted on the bills and coins are national heroes and leaders who have shaped Jamaica’s history. This cultural connection makes the currency more than just a means of exchange; it is a representation of Jamaica’s struggles, triumphs, and spirit of independence.
- National Heroes: Icons like Marcus Garvey, Nanny of the Maroons, and Samuel Sharpe appear on Jamaican currency, reinforcing the island’s rich heritage and reminding citizens of their shared history.
7. The Future of the Jamaican Dollar
As Jamaica continues to navigate the global economy, efforts are being made to stabilize the value of the Jamaican dollar. Recent years have seen improvements in economic growth and reductions in inflation, which could help to strengthen the currency in the future.
- Digital Currency: In 2022, Jamaica introduced its Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), known as JAM-DEX, in an effort to modernize the economy and promote financial inclusion. The launch of JAM-DEX represents a new frontier for the country, as it embraces digital transformation while addressing the challenges of traditional currency.
In 2023, Jamaica introduced a new series of polymer banknotes that reflect significant upgrades in both design and security features. This was the first major redesign since 1969, and the new notes were released to improve durability and counterfeiting resistance while honoring Jamaica’s rich cultural and historical legacy.
Here’s a breakdown of the new banknotes and the individuals featured on them:
- $50 Note: This features two National Heroes, George William Gordon and Paul Bogle, who were instrumental in the fight for civil rights and justice during Jamaica’s colonial period.
- $100 Note: Marcus Garvey, Jamaica’s first National Hero and a global icon of black empowerment and Pan-Africanism, stands alone on this note.
- $500 Note: This showcases Nanny of the Maroons, a revered leader of the Maroon resistance against the British, and Sam Sharpe, who led the Christmas Rebellion in the fight against slavery.
- $1000 Note: The images of Alexander Bustamante and Norman Manley, key figures in Jamaica’s move toward independence, are paired together on this note.
- $2000 Note: A new denomination, this note features Michael Manley and Edward Seaga, two former prime ministers who played crucial roles in shaping modern Jamaica’s political and economic landscape.
- $5000 Note: The highest denomination features Hugh Shearer and Donald Sangster, both of whom served as Prime Ministers of Jamaica.
In addition to featuring national heroes and key historical figures, these polymer notes are more durable, lasting longer than traditional paper money. They also include enhanced security measures, such as tactile features for the visually impaired, holographic foils, shimmering gold and silver inks, and UV-sensitive elements
These design improvements not only aim to boost the security and usability of the currency but also celebrate Jamaica’s rich history and national pride.
Conclusion
The Jamaican dollar is more than just a currency; it reflects the country’s vibrant history, economic challenges, and aspirations for the future. Whether you’re planning a trip to Jamaica or simply interested in learning about global currencies, understanding the Jamaican dollar offers a deeper appreciation of the island’s culture, resilience, and ongoing economic evolution.